Grain Structure of a Casting
The solidification from a liquid to room temperature occurs in 3 stages – contraction of the liquid steel, liquid to solid contraction and contraction of the solid to room temperature.
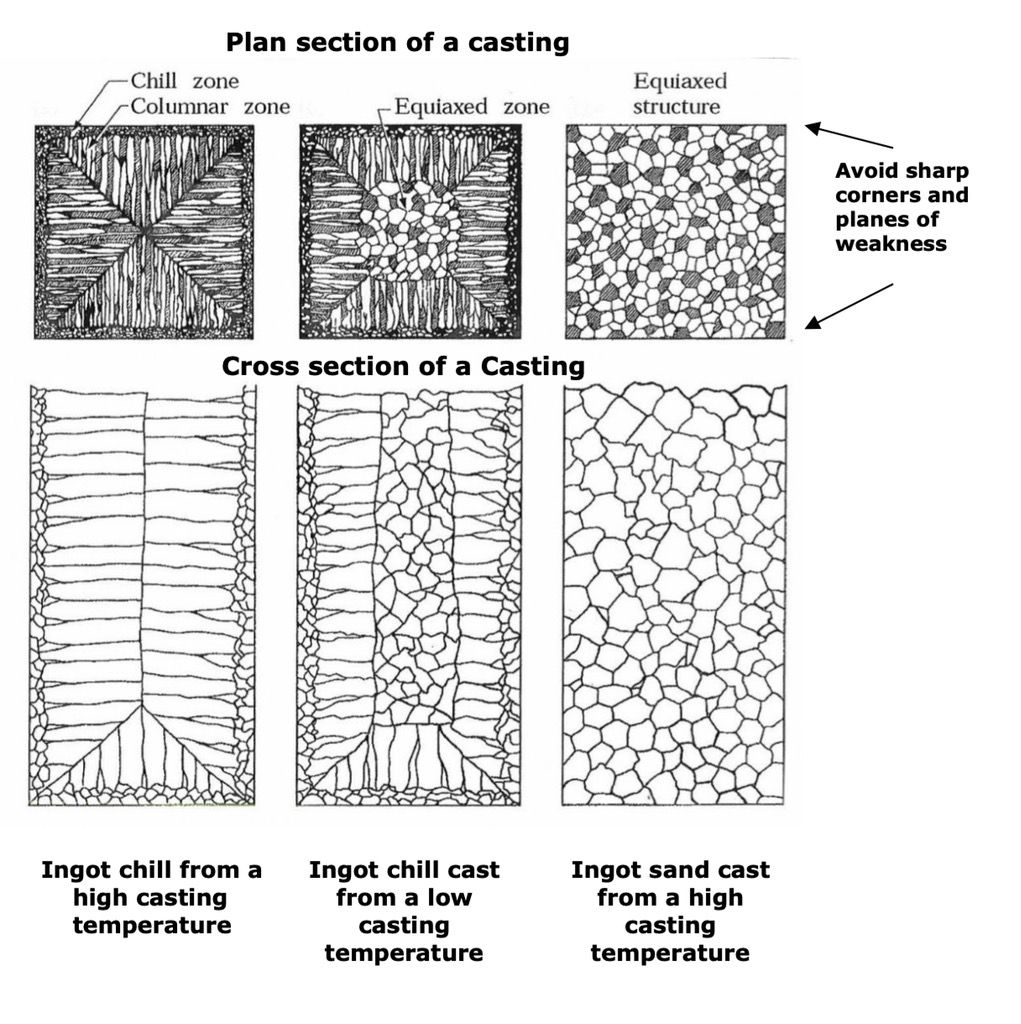
Stage 1 - During the liquid to solid contraction dendrite crystals begin to grow from the mould face. The first crystals are formed close to the wall of the mould and comprise of the chilled layer. These have the smallest grain structure
Stage 2 - The liquid to solid contraction is the next stage and it is the growth of dendritic crystals perpendicular to the mould wall. They grow in an elongated manner and are called columnar crystals. The factors that affect these crystals are thermal properties of the mould, the liquidus to solidus range of the metal, the thermal conductivity of the solidifying metal and the teeming temperature.
Stage 3 - When the temperature of the remaining liquid metal starts to fall and the cooling rate slows, directional growth stops and the final solidification takes place with the formation of equiaxal grains.
A crystal dendrite is a crystal that develops with a 20 typical multi- branching tree-like form.
Solidification of the metal in an ingot mould is accompanied by a reduction in volume as the temperature falls. As the metal cools from the outside first, the last liquid is at the centre towards the top and it is in this area that the final shrinkage takes place. Any impurities in the metal also float to the top due to their lower specific density and melting point and gather at the top centre of the ingot.
In a narrow end up ingot, the solidifying metal contracts during cooling to form sinks in the top of the ingot this is known as ‘primary pipe’ and the shrinkage within the ingot is known as ‘secondary pipe’. One way of reducing this is to place a refractory* top on to the iron mould to reduce heat loss, this is often referred to as a ‘hot top’.
Some impurities or evolved gas may be trapped in the ingot which may form defects during later processing.
Refractory definition: A refractory material is one that retains its strength at high temperatures.